Table of Contents
Definition of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality: The History of 40 Years
The first augmented reality system was developed in 1968 by Evan Sutherland as part of his research at MIT, the prestigious Boston University. At the time, it was a helmet with two lenses at eye level. It was connected to the computer by a pronounced arm, hence the nickname at the time: Sword of Damocles.
In this experiment, the 3D cube is displayed through a lens. The computer recalculates the image and viewing angle to track the user’s head movements. This tool lays the foundation for augmented reality.
In the 1980s, HUD systems (head-up display or heads-up vision) were developed, especially in the military. This system enables the display of specific information through a small transparent screen located in the pilot/driver field of view. These HUDs are currently found in some vehicles to display information such as speed, destination route, or encounter signals.
Subsequently, NASA also developed an augmented reality headset that would determine what Microsoft HoloLens would look like 30 years later. Lightweight but requires embedded computing, which allows device operators to override information on physical elements. Many other similar projects come to light.
The term “augmented reality” was not mentioned until the ’90s. In fact, two Boeing employees, Tom Cowdell and David Mitchell developed a device for group employees working on production lines. This system makes it possible to add a layer of information on certain elements in the chain and set a technical plan on the physical element.
In 1994, Rekimoto and Takashi, two scientists working in the Sony computer lab, developed Navicom, the first augmented reality system capable of reading markers. Very basic and fast, it allows you to launch text information that is realistically generated by a HUD-fitted helmet. Markers become reference support for fixing virtual elements in the real world by providing very fast response times.
So,
What is Augmented Reality or AR?
Augmented reality (AR) provides interaction between the virtual environment and the physical world, allowing both to interact through technology such as AR cameras, AR Lens, webcam, smart devices (iOS or Android), tablets, etc.
In other words, AR embodies virtual objects in a physical context and presents them to the user using the interface of the virtual environment with the support of technology. This resource is revolutionizing the way we handle our tasks (and even the ones we assign to machines).
In this way, we can say that augmented reality is characterized by:
- Combine real and virtual worlds;
- Providing real-time conversations;
- It adapts to the environment in which it is embedded;
- Interact with all the physical capabilities of the environment (in three dimensions).
Have you noticed that we refer to virtual reality as an integral part of augmented reality? This is because AR and VR are two different concepts, although generally confusing, in most cases, they work together. We have another article covering the difference between AR and VR which we will mention later.
How does Augmented Reality(AR) work?
The main goal of AR technology is the integration between the real (physical) world and the virtual world. Therefore, in order to reproduce augmented reality, 3 basic components are required:
- A real object serves as a reference to the description and structure of a virtual object.
- The existence of a device with a camera like a mobile phone to transmit an image of a real object.
- The software is responsible for interpreting the signal transmitted by the camera.
Through the camera, the actual object is transmitted to the software, which receives the image and combines it with 3D projections.
In turn, the projections are embedded into the image and superposed in the physical environment, showing the user the AR result.
What are the differences between augmented reality and virtual reality?
Although they have a similar name, their characteristics and intentions are very different.
While virtual reality creates an entirely new environment from the real world, augmented reality incorporates digital components into the physical world around us.
Both require a technical intermediary to access, however, they provide users with completely different experiences.
Virtual reality replaces the “real” location with 100% virtual content. This type of technology allows, for example, games, scenarios, and environments where the user interacts, moves, and interacts with fully digital content through complete immersion. For the detailed differences between AR and VR click here.
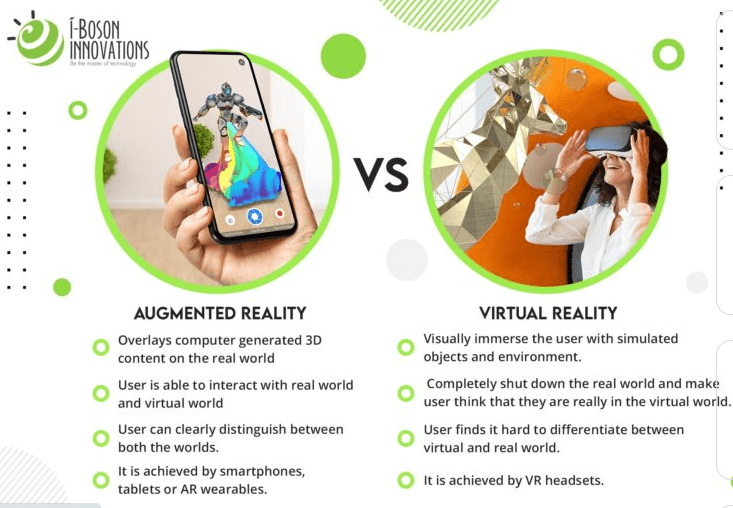
Augmented reality, on the other hand, projects information (such as images, graphics, letters, text) into the real world, giving it a new perspective on physical space.
A practical example is the game Pokémon Go, in which the characters must be captured, capturing the environment in which the user plays a part of that space.
What are the advantages of Augmented Reality?
Many of the most popular applications of augmented reality are intended for entertainment — such as sports — and companies in various fields (education, medicine, fashion, real estate, etc.) can also implement it, for example, in the development of their products and in their marketing strategies.
Augmented reality creates many opportunities and can completely change the way brands approach and engage their customers.
Product Details & Development
AR enables the customer to better interact with a product, its features, features, and functional details and, therefore, to know it well before they purchase it.
This allows the company to reduce its costs with the production of models and reduce conditions such as conversion and revenue.
In addition, it offers the customer new perspectives on the product, allowing them to use custom parameters to simulate their use and interaction.
Let’s look at a practical example: Imagine you are looking for shoes in Google Shopping and you have found a unique model, but, before you click “Buy”, you want to know if it fits in some of your outfits. What does it look like?
Although this may seem impossible, Google has already developed this type of augmented reality function using the camera, as we show you in the picture. The name of the app is Google Lens.
Interactive marketing experience
Already applied to marketing, be it traditional or digital, augmented reality strengthens the relationship between the public and the brand, winning new customers and promoting public awareness of the innovative company.
A few years ago, National Geographic created the augmented reality app, which shocked many in London.
The action turned the interior of the shopping center into a place where dolphins could swim with pet leopards or watch dinosaurs roaming among them.
5 augmented reality examples for our daily life
It does not take much effort to find practical examples of augmented reality and in many cases can already be implemented in our daily routine. For entertainment, to optimize tasks, to facilitate processes, AR is always there.
Next, we will give you 4 practical examples of its use.
1. Google Lens Augmented Reality
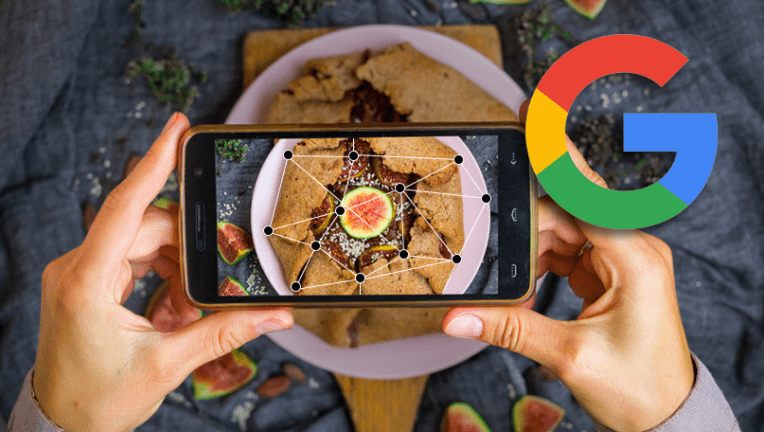

Google Lens is a set of vision-based computing capabilities that you can use to capture what you see, copy or translate text, identify plants and animals, identify places or menus, search for products, and more. Search, find and capture identical images. Other useful activities.
Google Lens lets you see what you see. Using a photo, your camera, or almost any image, the lens can help you quickly find similar images and related content by integrating the results across the Internet.
The lens compares objects in your image to other images and ranks those images based on their similarity and relevance to objects in the original image. The lens also uses your perception of the objects in your image to find other relevant results from the web. Other help references, such as words, language, and other metadata, may also be used on the image host site to determine lens ranking and relevance.
When analyzing an image, the lens often produces a number of potential outcomes and ranks the potential relevance of each outcome. The lens sometimes limits these possibilities to a single result. Suppose the lens is looking at a dog that is probably identified as 95% German Shepherd and 5% Corgi. In this case, the lens shows results only for a German Shepherd, the lens is likely to be identical.
2. Application filters
Snapchat and Instagram filters are a perfect example of the augmented reality that has gone viral.
The app algorithm calculates the landmarks in the camera image based on the thousands of photos already collected. In this way, it manages to incorporate the “digital drawing” of the filter as a whole.
It uses a kind of 3D mask to understand the user’s movements, so even when we move or change location, the filter is realistic.
3. QR code

The QR code is an alternative to the traditional barcode. A label made of black and white squares can store a lot of information, such as the origin and technical characteristics of the product.
When the camera captures an image of the image, the software “translates” that content. The result can be a text, image, or link to a website.
4. Google Translate
The Google Translate app lets you use a picture taken with your mobile phone camera to identify languages and automatically translate words and phrases written on signs and panels.
Google translate is a very easy resource to use, & can be very useful in different situations.
5. Google Maps

Furthermore, in Google products, the Google Maps application allows you to use augmented reality to make navigation and receive navigation guides on how to reach a destination.
The feature, called Live View, uses a mobile phone camera to project turning directions into the real world.
Conclusion
Augmented reality is already a trend in various markets and is increasingly being used by companies around the world, making the use of information and products more practical, easier, and faster.
The use of AR technology will undoubtedly have a greater impact in the years to come, transforming the shopping experience into a more personalized experience.
Therefore, it is possible for a customer to be loyal to a brand that exhibits an effort to make a simple purchase fun and interactive.
If You find this content worth reading. don’t forget to share and discuss. Thank You
Other Interesting Reads:
What Is Marketing Automation And How Does It Work?
How Artificial Intelligence [AI] is transforming Digital marketing’s future?
Important Prerequisite For An E-commerce Website