Table of Contents
What is DKIM for Email?
DomainKeys Identified Mail, or DKIM, is a technical standard that helps protect email senders and recipients from spam, spoofing, and phishing. This is a form of email authentication that allows the company to take responsibility for the message verified by the recipient.
In particular, it uses a process called “public-key cryptography” to verify that an email message has been sent from an authorized mail server to detect forgery and protect against malicious emails such as spam. Distribution can be stopped. It complements SMTP, the basic protocol used to send an email, as it does not have any authentication mechanism by itself.
How does DKIM work?
DKIM works by adding a digital signature to the header of the email message. The signature is verified against the public cryptographic key in the organization’s Domain Name System (DNS) record. In general terms, the process works like this:
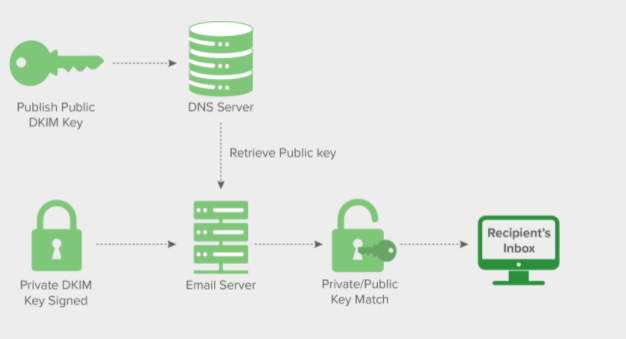
The domain owner publishes the cryptographic public key to the domain’s composite DNS record as a specially formatted TXT record.
When a mail message is sent through an outbound mail server, the server generates and adds a unique DKIM signature header to the message. This header contains two cryptographic hashes, one of the specified headers and one (or part) of the message body. The header contains information about how the signature was created.
When the inbound mail server receives the incoming email, it sees the sender’s public DKIM key. The inbound server uses this key to decrypt the signature and compares it with the newly computed version. If the two values are matched, the message proves to be authentic and does not change in transit. Learn about CAN-SPAM.
What is a DKIM signature?
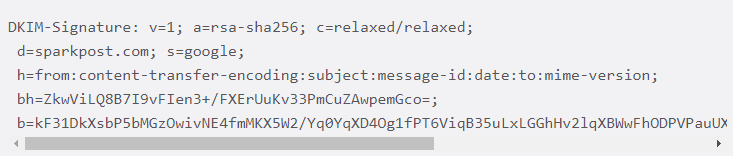
The DKIM signature is a header attached to email messages. The header contains the values that allow the receiving mail server to verify the email message by looking at the sender’s DKIM key and using it to verify the encrypted signature. It looks like this:
Set up DKIM to prevent email spoofing
- Make your email more secure and protect your domain
- Use the DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) standard to help prevent spoofing on outgoing messages sent from your domain.
Email spoofing occurs when email content is altered to reveal a message from someone other than the original source. Spoofing is a common unauthorized use of email, so some email servers require DKIM to prevent email spoofing.
DKIM adds an encrypted signature to the header of all outgoing messages. Email servers that receive signed messages use DKIM to decrypt the message title and verify that it hasn’t changed since the message was sent. Learn New email marketing terms.
If you need more email security, we recommend setting up these security methods with DKIM:
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF) – SPF specifies which domains your organization can send messages to.
- Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Compliance (DMARC) – DMARC specifies how your domain handles suspicious emails.
The DKIM signature header packs a lot of information because it is intended for automated processing. As you can see in this example, the tag = value in the header is a list of components. Notable tags include “d =” for the signing domain, “b =” for the original digital signature, and “bh =” for the hash, which is verified by recalculation using the sender’s public key.
Signatures are message-by-message by definition, but these key elements are in every DKIM signature header.
How does DKIM relate to SPF, DMARC, or other standards?

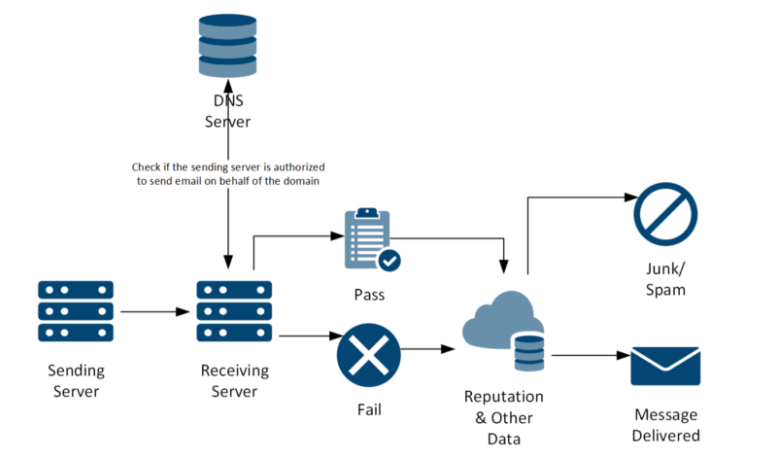
DKIM, SPF, and DMARC are all standards that enable different aspects of email authentication. They solve complementary problems.
SPF allows senders to define which IP addresses are allowed to send mail for a specific domain.
DKIM provides an encryption key and a digital signature that verifies that the email message has not been duplicated or altered. Learn about email autoresponders.
DMARC integrates SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms into a common framework and allows domain owners to declare how they want to manage email from that domain if they fail the authorization test.
Do I need a DKIM?
If you are a business that sends commercial or transactional emails, you must implement one or more email authentication policies to verify that the email actually came from you or your business. Properly configuring email authentication criteria is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your delivery. In any case, it only goes so far in it; Sparkpost and other email experts also recommend implementing SPF and DMARC to define a more complete email authentication process.
Hope You find this content helpful. Don’t forget to share and Leave Your comments. Thank You



2 Comments