Email is emerging as one of the most valuable services on the Internet today. Most Internet systems use SMTP as a way to transfer mail from one user to another. SMTP is the push protocol used to send emails, while POP (Post Office Protocol) or IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is used to retrieve emails from the receiver.
Table of Contents
SMTP Basics
SMTP is an application layer protocol. The client who wants to send the mail opens the TCP connection to the SMTP server and then sends the mail across the connection. The SMTP server is always in listening mode. The SMTP process initiates the connection through port 25 as soon as it hears a TCP connection from the client. The client process sends the mail as soon as the TCP connection is successfully established.
SMTP Highlights:
- SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- SMTP is a set of communication guidelines that allow the software to transmit electronic mail over the Internet, also known as a simple mail transfer protocol.
- It is a program used to send messages to other computer users based on email addresses.
- It provides and supports mail exchange between users on the same or different computers:
- It can send a message to one or more recipients.
- Sending messages can include text, voice, video, or graphics.
- It can also send messages to networks outside the Internet.
The main purpose of SMTP is to establish communication rules between servers. Servers have a way of identifying themselves and declaring what kind of communication they are trying to communicate. They also have a way of handling errors such as an incorrect email address. For example, if the recipient’s address is incorrect, the server will receive a reply with an error message.
Components of SMTP

First, we divide the SMTP client and SMTP server into two components, the User-Agent (UA) and the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). The user agent (UA) prepares the message, creates the envelope, and then covers the message. The Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) transfers this mail over the Internet.

SMTP allows a more complex system by connecting a relaying system. Instead of an MTA on the sending and receiving side, you can add more MTAs by acting as a client or server to relay the email.
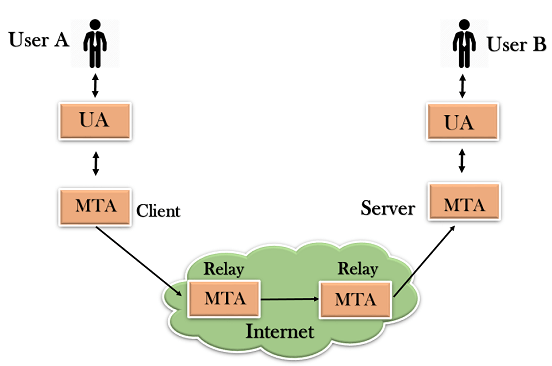
Relay systems without TCP/IP protocol can also be used to send email to customers and this is accomplished by using the mail gateway. Mail Gateway is a relay MTA used to receive emails.

Functions of SMTP
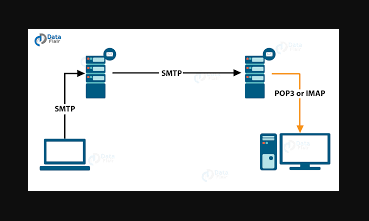
Mail structure: A user sends an e-mail by composing an electronic mail message using the Mail User Agent (MUA). Mail User Agent is a program used to send and receive mail. The message consists of two parts: the body and the title.
Summary The main part of the message, however, is the header, which contains information such as sender and recipient address. The header also contains detailed information such as the content of the message. In this case, part of the message is like a letter and the title is like an envelope containing the recipient’s address.
Submitting mail: After composing the email, the mail client submits the completed e-mail to the SMTP server using SMTP via TCP port 25.
Mail Delivery: E-mail addresses have two parts: the recipient’s username and the domain name. For example, vicky@gmail.com, where “Vicky” is the recipient’s username and “gmail.com” is the domain name.
If the domain name of the recipient’s email address and the domain name of the sender are different, the MSA sends the mail to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). To transmit email, MTA finds the target domain. It checks the MX record from the domain name system to get the target domain. The MX record contains the domain name and IP address of the recipient domain. Once the record is found, the MTA will connect to the Exchange server to transmit the message.
Receipt and processing of mail: After receiving the incoming message, the exchange server sends it to the incoming server (mail delivery agent), which stores the email waiting for the user to retrieve it.
Mail access and retrieval: Emails stored in MDA can be retrieved using MUA (Mail User Agent). MUA can be accessed using login and password.
SMTP commands
- Helo – identifies the client to the server, with a fully qualified domain name sent only once per session
- Mail – Enable message transfer, the domain’s fully qualified domain
- RCPT – follows the mail, identifies the addressee, usually the addressee’s fully qualified name, and uses one RCPT for each addressee for multiple addresses
- Data – Send data by line
You may also Like
What Is Email Harvesting & Is Email Harvesting Illegal?
What do You mean by Opt-In in Email Marketing?