Table of Contents
What is Return On Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is the financial ratio used by investors to calculate the return on their investment costs. It is usually measured as net income divided by the actual capital expenditure of the investment. The higher the ratio, the higher the profit earned. This guide breaks down the ROI principle, explains examples of how to calculate it,
Investment return (ROI) is a performance measure used to estimate the efficiency or profitability of an investment or to compare the potential of many different investments. ROI seeks to directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment relative to the investment price.
To calculate the ROI, the profit (or return) of the investment is divided by the investment cost. The result is expressed as a percentage or ratio.
ROI Key Highlights:
- Return on investment (ROI) is a well-known profitability metric used to estimate how well an investment has performed.
- ROI is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the net profit (or loss) of the investment by its initial cost or expense.
- The ROI can be used to make apple-to-apple comparisons and rank investments in various projects or assets.
- ROI does not take into account holding time or expiration time, so it may miss out on the opportunity cost of investing elsewhere.
Formula To Calculate ROI?
The formula to calculate Return On Investment is as follows:
“Net return on investment” refers to the income from the sale of interest investments. Since ROI is measured as a percentage, it can be easily compared to the returns from other investments, allowing one to measure different types of investments.
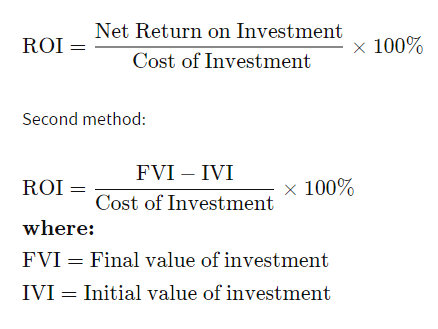
ROI Example


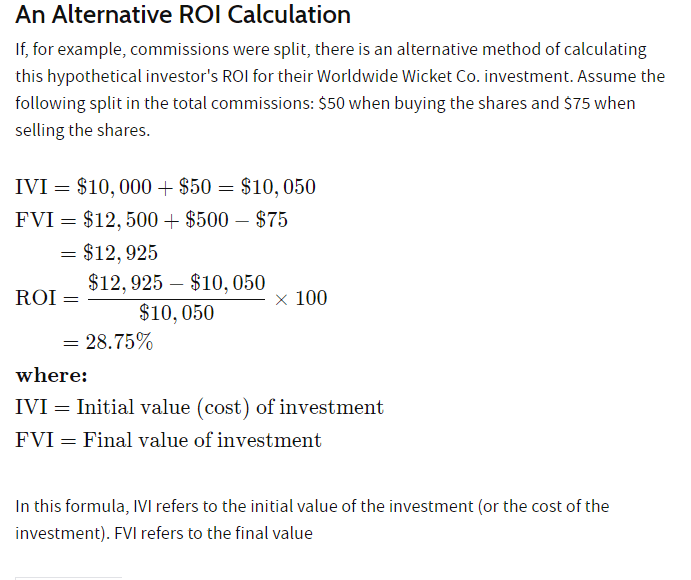
An alternative method to calculate ROI,
What are the benefits of ROI?
The advantages of the ROI ratio are as follows:
It is usually easy to calculate: Specific data is required to complete the calculation, which must be available in all financial statements or balance sheets.
Comparative analysis capability: Due to its wide use and ease of calculation, more comparisons can be made for investment returns between firms.
Profitability measures: ROI is the net income from investments made in a particular business entity. It provides a better measure of profitability by company or team.
What is the limitation of ROI?
ROI is one of the most common investments and profitability ratios used today. However, it has some drawbacks. The limitation of return on investment include:
Failure to take time into account in the equation: On the surface, a higher ROI appears to be a better investment. But an investment that takes 10 years to generate more ROI than any other investment takes only one year to generate a slightly lower ROI.
ROI calculations may vary between businesses: Because there are different equations for calculating ROI, not every business uses the same, making comparisons between investments irrelevant.
Managers can only select investments with a large ROI: Some investments with low ROI still increase business value. But sub-optimal options can lead to poor allocation of resources.
There is no way to calculate non-financial benefits: Using ROI as an example for new computers, a business can calculate net profit and total cost.
ROI using specific dollar amounts. However, getting new computers can make it harder to calculate the moral value of better employees. However, businesses can calculate ROI for such invisible purposes by labeling these calculations as soft ROIs, while calculations with direct dollar amounts are called hard ROIs.
What is a good ROI?
What qualifies as a “good” ROI depends on factors such as the investor’s risk tolerance and the time required to provide a return on investment. Since everything else is equal, investors who are more risk-averse will accept a lower ROI instead of taking lower risks. Similarly, investments that take longer to pay off generally require a higher ROI to be attractive to investors.
Which industry has the highest ROI?
Historically, the average ROI for the S&P 500 has been 10% per year. In that, however, it varies a lot depending on the industry. For example, in 2021, most technology companies will receive an annual return of more than this 10% threshold. Meanwhile, companies in other industries such as energy companies and utilities produced very low ROI and in some cases suffered losses for over a year. 2 Over time, it is common for industry average ROIs to change due to factors such as increased competition, technological changes and changes in consumer preferences. Also, Learn about return on advertisement spend (ROAS)
Conclusion
ROI is a simple and clear metric of investment returns. This metric has some limitations that do not take into account the holding period of the investment and are not adjusted for risk. However, despite these limitations, the ROI is still used by key metric business analysts to evaluate and rank investment options. Learn about DOOH advertising.
Hope! you find this information helpful. don’t forget to share and leave comments in order to support our work. Thank you.




8 Comments